|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
炭素材料の構造解析
炭素材料の構造は、一般的に複雑で解析が難しく、正確に構造を把握できていません。コンピューターを利用して分析結果を解析し、構造の特定を目指しています。 (1)分光分析・顕微鏡による解析(ナノカーボン材料の欠陥量とサイズの制御・欠陥除去・官能基の移動現象・ガス化機構の解明): ナノカーボン材料には官能基に加え、空孔や、5、7員環(Stone-Thrower-Walesなど)、ジグザグエッジ、アームチェアエッジなどの欠陥が存在します。これらの欠陥構造を光電子、赤外、透過型電子顕微鏡、Raman分光分析などで解析しています。 炭素材料にはベーサルとエッジがあり、特にベーサルへの空孔欠陥の導入を行い、この構造を解析しています。炭素材料の欠陥は、機械的、電気的、熱的特性に大きな影響を与えます。これらの欠陥を除去することにより理論に近いナノカーボン材料を調製することを目指しています。 さらに、加熱による炭素材料表面(ベーサル面とエッジ面)の官能基の移動現象と、ガス化について研究しています。 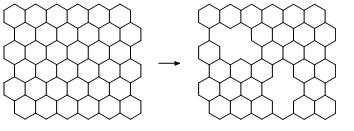
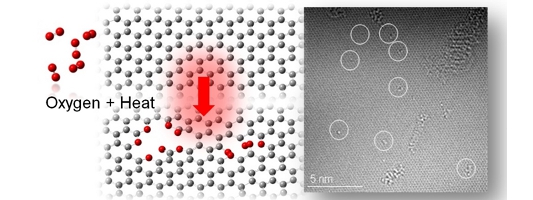
空孔欠陥導入過程
Sub-nanometer vacancy defects introduced on graphene by oxygen gas ・ Y. Yamada, K. Murota, et al., "Subnanometer vacancy defects introduced on graphene by oxygen gas", J Am Chem Soc 136(6)(2014)2232-2235.
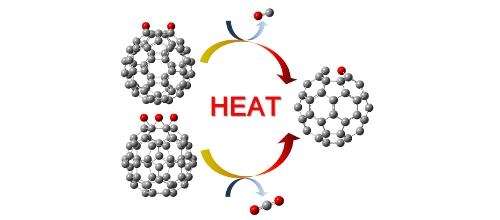
Fig. Pyrolysis of epoxidized fullerenes (Calculated by Gaussian03) ・ J. Kim, Y. Yamada*, et al., "Oxygen migration and selective CO and CO2 formation from epoxidized fullerenes", J Phys Chem C 118(13)(2014)7085-7093. ・ J. Kim, Y. Yamada*, et al., "Pyrolysis of epoxidized fullerenes analyzed by spectroscopies", J Phys Chem C 118(13)(2014)7076-7084. (2)量子化学計算と実測を用いた欠陥構造解析(XPS・IR・Raman・NMR・UV・TEM): 炭素材料のベーサル面、エッジ面には様々な種類の官能基や点欠陥などの欠陥が存在します。炭素材料の特性を最大限に引き出すためにはこの官能基の完全解明が求められます。この解明のため含酸素官能基、含窒素官能基、5員環、その他の欠陥のXPSやIR、Raman、NMR、UVスペクトル、TEM像のシミュレーションを行っています。 Gaussianという計算ソフトを利用して100種類以上の異なる炭素材料の構造を組み立てて、実際に装置で得られる分析結果を計算によりシミュレーションすることに成功しました。これほど多くの炭素材料の構造をシミュレーションした例はなく、今後の炭素材料に関する多くの研究において重要な結果が得られました。
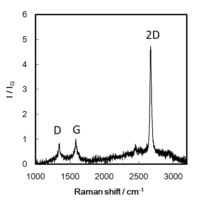
グラフェンの欠陥の種類 グラフェンのTEM像 グラフェンのラマンスペクトル
OHが導入されたグラフェン 左図のC1s XPSスペクトルのシミュレーション結果 ・ Y. Yamada, et al., "Analysis of heat-treated graphite oxide by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy", J Mater Sci 48 (2013) 8171-8198. ・ J. Kim, Y. Yamada, et al., "Pyrolysis of epoxidized fullerenes analyzed by spectroscopies", J. Phys. Chem. C 118 (2014) 7076-7084. ・ Y. Yamada, et al.,"Nitrogen-containing graphene analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy", Carbon 70 (2014) 59-74. ・ J. Kim, Y. Yamada*, M. Kawai, T. Tanabe, S. Sato, "Spectral change of simulated X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy from graphene to fullerene", J. Mater. Sci. 50 (2015) 6739-6747. ・ Y. Yamada*, S. Sato, "Structural analysis of carbon materials by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy using computational chemistry (Review by awardee)", Tanso 269 (2015) 1-9. ・ Y. Yamada*, K. Murota, R. Fujita, J. Kim, A. Watanabe, M. Nakamura, S. Sato, K. Hata, E. Peter, J. Ciston, C. Song, K. Kim, W. Regan, W. Gannett, A. Zettl, "Subnanometer vacancy defects introduced on graphene by oxygen gas", J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136(6) (2014) 2232-2235. ・ Y. Yamada*, S. Masaki, S. Sato, Brominated positions on graphene nanoribbon analyzed by infrared spectroscopy, J. Mater. Sci. 55 (2020) 10522-10542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04786-1 ・ T. Kato, Y. Yamada*, Y. Nishikawa, H. Ishikawa, S. Sato, Carbonization mechanisms of polyimide: methodology to analyze carbon materials with nitrogen, oxygen, pentagons, and heptagons, Carbon 178 (2021) 58-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.090 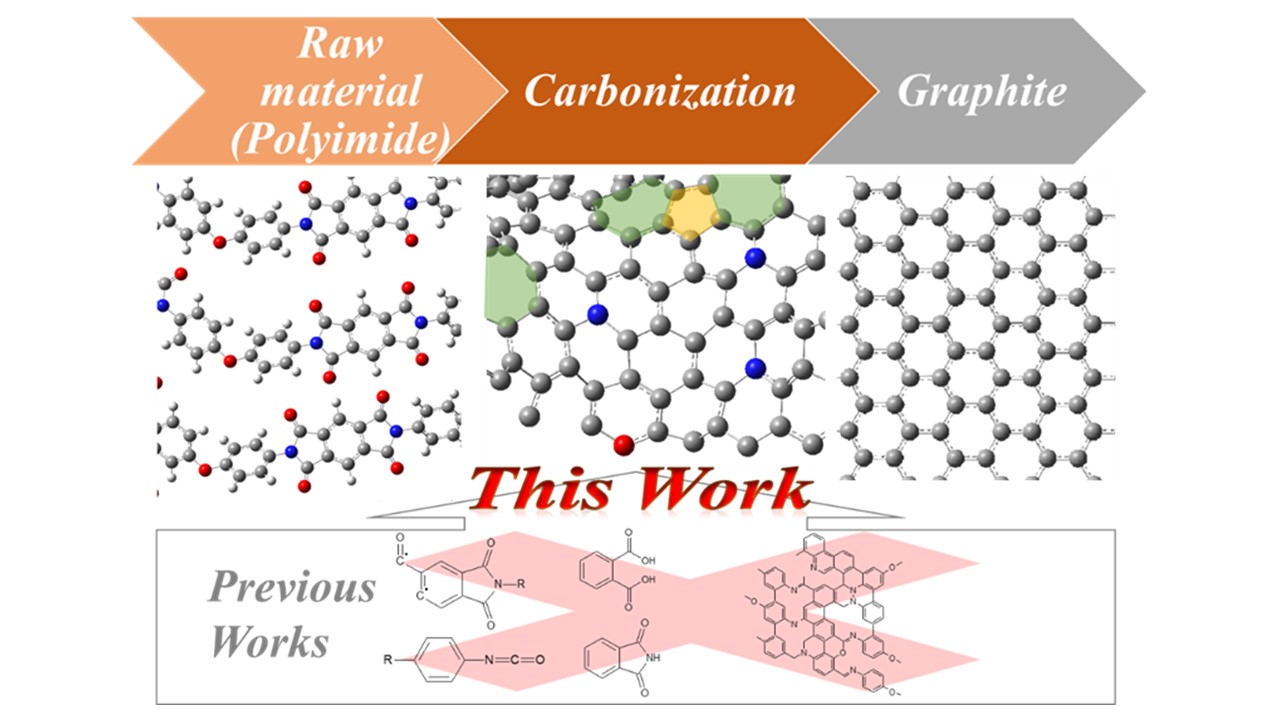
Reprinted with permission. Copyright (2021) Elsevier. ・ Y. Yamada*, H. Tanaka, S. Kubo, S. Sato, Unveiling bonding states and roles of edges in nitrogen-doped graphene nanoribbon by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Carbon 185 (2021) 342-367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2021.08.085 Degree of carbonization can be estimated from these peak positions. 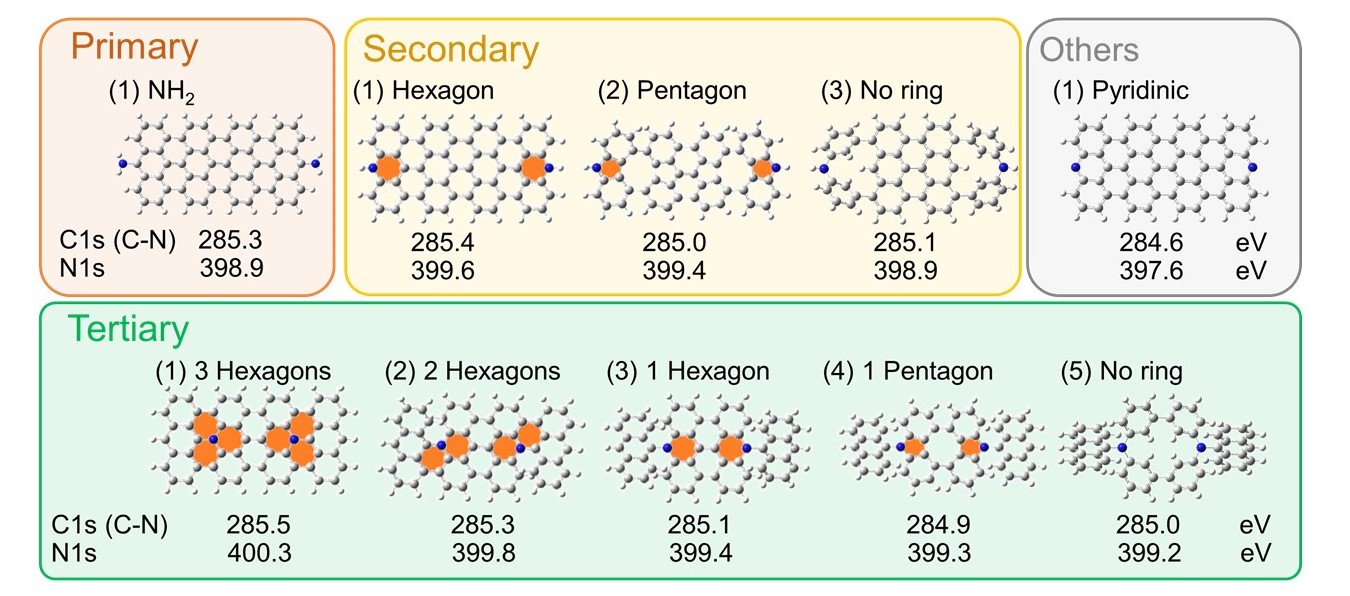
Reprinted with permission. Copyright (2021) Elsevier. ・ K. Mori*, J. Kim, S. Kubo, Y. Yamada*, Effects of molecular shapes, molecular weight, and types of edges on peak positions of C1s X-ray photoelectron spectra of graphene-related materials and model compounds, J. Mater. Sci. 57 (2022) 15789-15808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07599-6 Free for view only.--> "Effects of molecular shapes, molecular weight, and types of edges on peak positions of C1s X-ray photoelectron spectra of graphene-related materials and model compounds" |